ROS2(Robot Operating System 2)是一个用于机器人和自动化系统开发的开源软件平台。
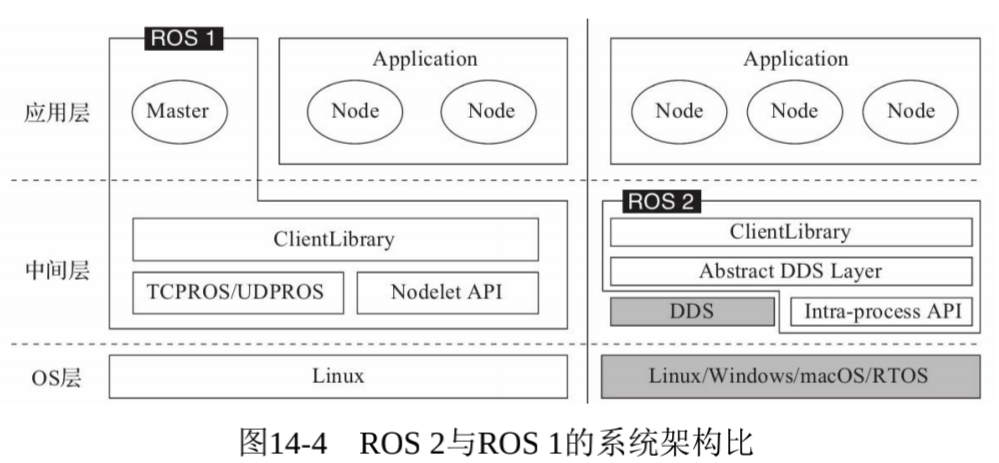
ROS2的系统架构
OS层
OS层,在ROS2中可以构建在linux上,也可以构建在其它系统上,甚至是没有操作系统的裸机。
中间层
ROS1的通信系统基于TCPROS/UDPROS,而ROS2的通信系统基于DDS。DDS是一种分布式实时系统中数据发布/订阅的标准解决方案。
应用层
ROS1依赖于ROS Master,而在ROS2中,节点之间使用一种称为“Discovery”的发现机制来帮助彼此建立连接。
DDS DDS是“Data Distribution Service”的缩写,是一种面向实时和嵌入式系统的标准化、可互操作的消息传递协议。DDS旨在实现在分布式环境中高效且可扩展地交换数据。它通常用于需要高性能、低延迟和可靠性的系统。它提供了一个中间件层,抽象了分布式通信的复杂性,使开发人员更容易构建可扩展和可靠的系统。
DDS的主要特点包括:
发布-订阅模型:
DDS采用发布-订阅通信模型。数据生产者(发布者)发布信息,数据消费者(订阅者)接收他们感兴趣的信息。
分散式架构:
DDS设计为在分散式环境中工作,允许可扩展和容错的系统。没有中央代理,数据直接在发布者和订阅者之间交换。
实时和服务质量(QoS):
DDS支持实时通信,并提供丰富的服务质量(QoS)参数。这些参数允许微调通信特性,如可靠性、持久性和延迟。
动态发现:
DDS支持发布者和订阅者的动态发现。这意味着实体可以加入或离开网络,系统会动态地适应这些变化。
数据中心:
DDS以数据为中心,侧重于高效交换数据,而不关注底层网络或通信基础设施的详细信息。
语言中立:
DDS被设计为语言中立,允许使用不同编程语言编写的应用程序无缝通信。
ROS 2中常见的几种通信方式:
话题(Topics) :
话题是ROS中最常用的通信方式之一。它允许节点以发布者-订阅者的模式进行消息传递。一个节点可以发布消息到一个话题,而其他节点则可以订阅该话题以接收消息。
服务(Services) :
服务是一种ROS中的双向通信方式,它允许节点之间进行请求-响应式的通信。一个节点可以提供一个服务,而其他节点则可以调用该服务来发送请求并接收响应。
参数(Parameters) :
参数是用于配置节点行为和功能的数据。ROS 2中的参数服务器允许节点动态地设置和获取参数值,以调整节点的行为。参数可以在运行时进行更改,并且可以通过参数事件来监视参数的变化。
行为(Actions) :
行为是ROS 2中的高级通信机制,它允许节点执行复杂的、长时间运行的任务。行为通常用于需要一系列连续操作的场景,例如导航、操纵机器人臂等。
ros2下编译一个hello world程序 创建工作空间,在终端上创建一个工程文件夹名为hello_ws,并在src目录下创建一个ros包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 mkdir -p hello_ws/srccd hello_wscolcon build cd /srcros2 pkg create hello --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclcpp cd ~/hello_ws/src/hello_world/srcvi helloworld.cpp
编辑helloworld.cpp文件,并添加以下内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 #include <stdio.h> #include <rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp> int main (int argc ,char *argv[]) rclcpp::init (argc, argv); auto node = rclcpp::Node :: make_shared ("hello_world_node" ); RCLCPP_INFO (node->get_logger (),"Hello world" ); rclcpp::shutdown (); return 0 ; }
CMakeLists.txt文件加入以下内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 add_executable (hello_node src/helloworld.cpp)ament_target_dependencies(hello_node rclcpp) install (TARGETS hello_node DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME} )
最后,编译ROS包:
1 2 3 4 cd ~/hello_wscolcon build source install/setup.bash ros2 run hello helloworld
现在,就可以在ros2环境下打印出hello world。
面向对象和面向过程 面向对象的方式编写ROS2节点 将之前的的程序代码进行改写
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" class Node1 : public rclcpp::Node { public: Node1() : Node("node1") { RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(),"上班了"); } private: }; int main(int argc, char **argv) { rclcpp::init(argc, argv); //产生一个Node1节点 auto node = std::make_shared<Node1>(); //运行节点,并检测退出信号 rclcpp::spin(node); rclcpp::shutdown(); return 0; }
ros2节点发现与多机通信 如其他地方所解释的,ROS 2用于通讯的默认中间件是DDS。在DDS中,不同逻辑网络共享物理网络的主要机制称为域(Domain) ID。同一域上的ROS 2节点可以自由地相互发现并发送消息,而不同域上的ROS 2节点则不能。所有ROS 2节点默认使用域ID为0。为了避免在同一网络上运行ROS 2的不同计算机组之间互相干扰,应为每组设置不同的域ID。
选择域ID短版本 :
使用命令行界面(CLI)时,可以直接指定短域名称,例如ros2 param set。
短域名称较为简洁,适合在命令行中快速使用。
不需要指定完整的命名空间路径,只需提供短域名称即可。
例如,假设节点名为my_node,参数名为my_parameter,则短版本命令可以是ros2 param set my_node my_parameter 42。
选择域ID长版本 :使用编程接口时,需要提供完整的参数名称,包括节点名称和参数名称。
长版本的参数名称包含节点的全名(包括命名空间),以及参数的名称,用斜杠(/)分隔。
长版本的参数名称在编程接口中更为直观,方便程序员进行参数操作。
例如,假设节点名为my_node,参数名为my_parameter,则长版本参数名称为/my_node/my_parameter。
默认情况下,linux内核使用端口32768-60999作为临时端口。这意味着域ID 0-101 和 215-232 可以安全使用,而不会与临时端口发生冲突。临时端口范围可在Linux中通过在 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range 中设置自定义值进行配置。如果使用自定义临时端口范围,则可能需要相应地调整上述数字
ros2 消息 整体上ros2和ros1的创建是差不多的。
首先是建立软件包
1 2 3 4 5 6 mkdir -p work_ws/src cd work_ws colcon build cd src ros2 pkg create msg_pkg --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclcpp std_msgs cd msg_pkg/msg
编写字节的msg消息文件,例如Person.msg这里首字母要大写。
之后更改msg_pkg包中的CMakeLists.txt文件,加入
1 2 3 4 5 6 find_package (builtin_interfaces REQUIRED) find_package (rosidl_default_generators REQUIRED)rosidl_generate_interfaces(${PROJECT_NAME} "msg/Person.msg" DEPENDENCIES builtin_interfaces )
之后更改msg_pkg包中的Package.xml文件,加入
1 <member_of_group>rosidl_interface_packages</member_of_group>
工作空间目录下进行编译
ros2 话题 跟ros1是一样的,一个节点发布数据到某个话题上,另一个节点就可以通过订阅话题拿到数据,还可以是1对n,n对1,n对n的,或者自己发自己接收。
ros2下话题发布与订阅 接着前面的工程文件夹进行编写
发布文件名字:topic.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" #include "std_msgs/msg/string.hpp" class TopicPublisher01 : public rclcpp :: Node{ public : TopicPublisher01 () : Node ("publisher_node" ) { RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "启动pulisher" ); publisher = this -> create_publisher <std_msgs::msg::String>("/chatter" ,10 ); timer_ = this ->create_wall_timer (std::chrono::milliseconds (500 ), std::bind (&TopicPublisher01::publish_message, this )); counter_ = 0 ; } private : void publish_message () { auto message = std_msgs::msg::String (); message.data = "Hello ROS 2 " + std::to_string (counter_); publisher->publish (message); counter_++; RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "Publishing: '%s'" , message.data.c_str ()); } rclcpp::Publisher<std_msgs::msg::String>::SharedPtr publisher; rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_; size_t counter_; }; int main (int argc, char * argv[]) rclcpp::init (argc, argv); auto node = std::make_shared <TopicPublisher01>(); rclcpp::spin (node); rclcpp::shutdown (); return 0 ; }
订阅文件名字subscribe
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" #include "std_msgs/msg/string.hpp" void message_callback (const std_msgs::msg::String::SharedPtr msg) RCLCPP_INFO (rclcpp::get_logger ("subscriber_node" ), "Received message: '%s'" , msg->data.c_str ()); } int main (int argc, char *argv[]) rclcpp::init (argc, argv); auto node = rclcpp::Node::make_shared ("subscriber_node" ); auto subscription = node->create_subscription <std_msgs::msg::String>("/chatter" , 10 , message_callback); rclcpp::spin (node); rclcpp::shutdown (); return 0 ; }
CMakeLists.txt文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 cmake_minimum_required (VERSION 3.8 )project (example_topic)if (CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang" ) add_compile_options (-Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic) endif ()find_package (ament_cmake REQUIRED)find_package (rclcpp REQUIRED)find_package (std_msgs REQUIRED)if (BUILD_TESTING) find_package (ament_lint_auto REQUIRED) set (ament_cmake_copyright_FOUND TRUE ) set (ament_cmake_cpplint_FOUND TRUE ) ament_lint_auto_find_test_dependencies() endif ()ament_package() add_executable (topic_publish src/topic.cpp)ament_target_dependencies(topic_publish rclcpp std_msgs) add_executable (topic_subscribe src/subscriber.cpp)ament_target_dependencies(topic_subscribe rclcpp std_msgs) install (TARGETS topic_publish topic_subscribe DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME} )
编译后两个终端进行发布订阅:
ROS2实战(1个消息包1个发布订阅包) 1个软件包存储一个人的信息(名字和年龄),1个软件包负责发布和订阅这个消息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 mkdir -p work_ws/src colcon build cd src ros2 pkg create msg_pkg --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclcpp std_msgs cd msg_pkg/msg vi Person.msg # //文件内容为 string name int32 age #
之后更改msg_pkg包中的CMakeLists.txt文件,加入
1 2 3 4 5 6 find_package (builtin_interfaces REQUIRED) find_package (rosidl_default_generators REQUIRED)rosidl_generate_interfaces(${PROJECT_NAME} "msg/Person.msg" DEPENDENCIES builtin_interfaces )
之后更改msg_pkg包中的Package.xml文件,加入
1 <member_of_group > rosidl_interface_packages</member_of_group >
之后建立第二个软件包来发布订阅这个消息
1 2 3 cd ~/work_ws/src/ ros2 pkg create publish_subscribe --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclcpp std_msgs cd src
编写发布文件publisher.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" #include <msg_pkg/msg/person.hpp> using namespace std::chrono_literals; int main (int argc, char *argv[]) rclcpp::init (argc, argv); auto node = std::make_shared <rclcpp::Node>("person_publisher" ); auto publisher = node->create_publisher <msg_pkg::msg::Person>("person_topic" , 10 ); auto message = std::make_shared <msg_pkg::msg::Person>(); message->name = "john" ; message->age = 30 ; while (rclcpp::ok ()) { publisher->publish (*message); rclcpp::spin_some (node); std::this_thread::sleep_for (1 s); } rclcpp::shutdown (); return 0 ; }
编写订阅文件subscribe.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" #include "msg_pkg/msg/person.hpp" void personCallback (const msg_pkg::msg::Person::SharedPtr msg) int main (int argc, char *argv[]) rclcpp::init (argc, argv); auto node = std::make_shared <rclcpp::Node>("subscriber" ); auto subscription = node->create_subscription <msg_pkg::msg::Person>( "person_topic" , 10 , personCallback); rclcpp::spin (node); rclcpp::shutdown (); return 0 ; } void personCallback (const msg_pkg::msg::Person::SharedPtr msg) RCLCPP_INFO (rclcpp::get_logger ("rclcpp" ), "Received person: %s, %d" , msg->name.c_str (), msg->age); }
之后保存后,更改CMakeLists.txt文件,加入以下内容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 find_package (msg_pkg REQUIRED)add_executable (publisher src/publisher.cpp)add_executable (subscriber src/subscribe.cpp)ament_target_dependencies(publisher rclcpp msg_pkg) ament_target_dependencies(subscriber rclcpp msg_pkg) install (TARGETS publisher subscriber DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME} )
更改package.xml文件,加入以下内容
1 <depend > msg_pkg</depend >
之后在工作空间下进行编译
ROS2服务 首先创建一个工作空间,之后再src下创建一个装载srv消息的软件包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 mkdir -p service_ws/src cd service_ws colcon build cd src # 创建软件包 ros2 pkg create service_msgs --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclcpp std_msgs ros2 pkg create server_client --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclcpp std_msgs cd service_msgs mkdir srv cd srv vi Addtwo.srv # 编写msg的信息 int64 a int64 b --- int64 sum # 退出后修改CMakeLists.txt文件加入 find_package(rosidl_default_generators REQUIRED) rosidl_generate_interfaces($ {PROJECT_NAME} "srv/Addtwo.srv" DEPENDENCIES std_msgs ) # 同样也要修改package.xml文件,加入 <member_of_group>rosidl_interface_packages</member_of_group> cd ~/service_ws/src/server-client/src
编写服务器代码:server.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" class ServiceServer01 : public rclcpp::Node {public : ServiceServer01 (std::string name) : Node (name) { RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "节点已启动:%s." , name.c_str ()); } private :}; int main (int argc, char ** argv) rclcpp::init (argc, argv); auto node = std::make_shared <ServiceServer01>("service_server_01" ); rclcpp::spin (node); rclcpp::shutdown (); return 0 ; }
编写客服端代码:client.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" class ServiceClient01 : public rclcpp::Node {public : ServiceClient01 (std::string name) : Node (name) { RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "节点已启动:%s." , name.c_str ()); } private :}; int main (int argc, char ** argv) rclcpp::init (argc, argv); auto node = std::make_shared <ServiceClient01>("service_client_01" ); rclcpp::spin (node); rclcpp::shutdown (); return 0 ; }
之后编写包内的CMakeLists.txt文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 add_executable(service_client src/client.cpp) ament_target_dependencies(service_client rclcpp) add_executable(service_server src/server.cpp) ament_target_dependencies(service_server rclcpp) install(TARGETS service_server DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME} ) install(TARGETS service_client DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME} )
之后退出编译就成功了。
服务软件包调用消息包 在软件包中改写CMakeLists.txt文件,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 #加入 find_package(service_msgs REQUIRED) #改写 add_executable(service_client src/client.cpp) ament_target_dependencies(service_client rclcpp service_msgs) add_executable(service_server src/service_server_01.cpp) ament_target_dependencies(service_server rclcpp service_msgs)
packages.xml文件加入消息包进行依赖
1 <depend>example_interfaces</depend>
在代码中加入头文件就能调用了
1 #include "service_msgs/srv/addtwo.hpp"
ROS2组件 ROS 2中的组件(比如节点、插件等)可以被动态加载和卸载,这意味着它们可以在运行时进行加载,而无需重新编译整个系统。这种动态加载的机制使得ROS 2更加灵活,可以根据需要动态地修改系统的行为,而无需停机或重新启动。
组件的流程:
pluginlib是一个c + + 库,用于从ROS包中加载和卸载插件。插件是从运行时库加载的动态调用y可加载类 (即共享对象,动态调用y链接库)。使用pluginlib,不必将其应用程序与包含类的库显式链接-相反,pluginlib可以在任何时候打开包含导出类的库,而无需应用程序事先了解该库或包含类定义的头文件。插件可用于扩展/修改应用程序行为,而无需应用程序源文件。
1 sudo apt-get install ros-iron-pluginlib
组件的例程:
http://dev.ros2.fishros.com/doc/Tutorials/Pluginlib.html#create-the-base-class-package
ROS2动作(Action) Action的三大组成部分目标、反馈和结果。
目标:即Action客户端告诉服务端要做什么,服务端针对该目标要有响应。解决了不能确认服务端接收并处理目标问题
反馈:即Action服务端告诉客户端此时做的进度如何(类似与工作汇报)。解决执行过程中没有反馈问题
结果:即Action服务端最终告诉客户端其执行结果,结果最后返回,用于表示任务最终执行情况。
参数是由服务构建出来了,而Action是由话题和服务共同构建出来的(一个Action = 三个服务+两个话题) 三个服务分别是:1.目标传递服务 2.结果传递服务 3.取消执行服务 两个话题:1.反馈话题(服务发布,客户端订阅) 2.状态话题(服务端发布,客户端订阅)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 # 创建一个工作空间 mkdir -p chapt_ws/src cd chapt_ws/src ros2 pkg create robot_control_interfaces --build-type ament_cmake cd robot_control_interfaces mkdir action vi MoveRobot.action # # Goal:要移动的距离 float32 distance --- # Result: 最终的位置 float32 pose --- # Feedback:反馈状态 float32 pose uint32 status uint32 STATUS_MOVEING = 3 uint32 STATUS_STOP = 4 #
修改CMakeLists.txt文件
1 2 3 4 find_package (rosidl_default_generators REQUIRED)rosidl_generate_interfaces(${PROJECT_NAME} "action/MoveRobot.action" )
修改package.xml文件
1 2 <depend > rosidl_default_generators</depend > <member_of_group > rosidl_interface_packages</member_of_group >
回到src目录创立第二个软件包
1 2 3 4 cd ~/chapt_ws/src ros2 pkg create example_action_rclcpp --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclcpp rclcpp_action robot_control_interfaces cd example_action_rclcpp/include/example_action_rclcpp vi robot.h
编写功能函数的头文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #ifndef EXAMPLE_ACTIONI_RCLCPP_ROBOT_H_ #define EXAMPLE_ACTIONI_RCLCPP_ROBOT_H_ #include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" #include "robot_control_interfaces/action/move_robot.hpp" class Robot { public : using MoveRobot = robot_control_interfaces::action::MoveRobot; Robot () = default ; ~Robot () = default ; float move_step () bool set_goal (float distance) float get_current_pose () int get_status () bool close_goal () void stop_move () private : float current_pose_ = 0.0 ; float target_pose_ = 0.0 ; float move_distance_ = 0.0 ; std::atomic<bool > cancel_flag_{false }; int status_ = MoveRobot::Feedback::STATUS_STOP; }; #endif
在软件包下的src进行编写功能文件,客户端文件,服务端文件。
编写robot.cpp文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 #include "example_action_rclcpp/robot.h" float Robot::move_step () int direct = move_distance_ / fabs (move_distance_); float step = direct * fabs (target_pose_ - current_pose_) * 0.1 ; current_pose_ += step; std::cout << "移动了:" << step << "当前位置:" << current_pose_ << std::endl; return current_pose_; } bool Robot::set_goal (float distance) move_distance_ = distance; target_pose_ += move_distance_; if (close_goal ()) { status_ = MoveRobot::Feedback::STATUS_STOP; return false ; } status_ = MoveRobot::Feedback::STATUS_MOVEING; return true ; } float Robot::get_current_pose () return current_pose_; }int Robot::get_status () return status_; }bool Robot::close_goal () return fabs (target_pose_ - current_pose_) < 0.01 ; }void Robot::stop_move () status_ = MoveRobot::Feedback::STATUS_STOP; }
编写action_robot_01.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 #include "example_action_rclcpp/robot.h" #include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" #include "rclcpp_action/rclcpp_action.hpp" #include "robot_control_interfaces/action/move_robot.hpp" class ActionRobot01 : public rclcpp::Node { public : using MoveRobot = robot_control_interfaces::action::MoveRobot; using GoalHandleMoveRobot = rclcpp_action::ServerGoalHandle<MoveRobot>; explicit ActionRobot01 (std::string name) : Node(name) { RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "节点已启动:%s." , name.c_str ()); using namespace std::placeholders; this ->action_server_ = rclcpp_action::create_server <MoveRobot>( this , "move_robot" , std::bind (&ActionRobot01::handle_goal, this , _1, _2), std::bind (&ActionRobot01::handle_cancel, this , _1), std::bind (&ActionRobot01::handle_accepted, this , _1)); } private : Robot robot; rclcpp_action::Server<MoveRobot>::SharedPtr action_server_; rclcpp_action::GoalResponse handle_goal ( const rclcpp_action::GoalUUID& uuid, std::shared_ptr<const MoveRobot::Goal> goal) RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "Received goal request with distance %f" , goal->distance); (void )uuid; if (fabs (goal->distance > 100 )) { RCLCPP_WARN (this ->get_logger (), "目标距离太远了,本机器人表示拒绝!" ); return rclcpp_action::GoalResponse::REJECT; } RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "目标距离%f我可以走到,本机器人接受,准备出发!" , goal->distance); return rclcpp_action::GoalResponse::ACCEPT_AND_EXECUTE; } rclcpp_action::CancelResponse handle_cancel ( const std::shared_ptr<GoalHandleMoveRobot> goal_handle) RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "Received request to cancel goal" ); (void )goal_handle; robot.stop_move (); return rclcpp_action::CancelResponse::ACCEPT; } void execute_move (const std::shared_ptr<GoalHandleMoveRobot> goal_handle) const auto goal = goal_handle->get_goal (); RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "开始执行移动 %f 。。。" , goal->distance); auto result = std::make_shared <MoveRobot::Result>(); rclcpp::Rate rate = rclcpp::Rate (2 ); robot.set_goal (goal->distance); while (rclcpp::ok () && !robot.close_goal ()) { robot.move_step (); auto feedback = std::make_shared <MoveRobot::Feedback>(); feedback->pose = robot.get_current_pose (); feedback->status = robot.get_status (); goal_handle->publish_feedback (feedback); if (goal_handle->is_canceling ()) { result->pose = robot.get_current_pose (); goal_handle->canceled (result); RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "Goal Canceled" ); return ; } RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "Publish Feedback" ); rate.sleep (); } result->pose = robot.get_current_pose (); goal_handle->succeed (result); RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "Goal Succeeded" ); } void handle_accepted (const std::shared_ptr<GoalHandleMoveRobot> goal_handle) using std::placeholders::_1; std::thread{std::bind (&ActionRobot01::execute_move, this , _1), goal_handle} .detach (); } }; int main (int argc, char ** argv) rclcpp::init (argc, argv); auto action_server = std::make_shared <ActionRobot01>("action_robot_01" ); rclcpp::spin (action_server); rclcpp::shutdown (); return 0 ; }
编写action_control_01.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 #include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" #include "rclcpp_action/rclcpp_action.hpp" #include "robot_control_interfaces/action/move_robot.hpp" class ActionControl01 : public rclcpp::Node { public : using MoveRobot = robot_control_interfaces::action::MoveRobot; using GoalHandleMoveRobot = rclcpp_action::ClientGoalHandle<MoveRobot>; explicit ActionControl01 ( std::string name, const rclcpp::NodeOptions& node_options = rclcpp::NodeOptions()) : Node(name, node_options) { RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "节点已启动:%s." , name.c_str ()); this ->client_ptr_ = rclcpp_action::create_client <MoveRobot>(this , "move_robot" ); this ->timer_ = this ->create_wall_timer (std::chrono::milliseconds (500 ), std::bind (&ActionControl01::send_goal, this )); } void send_goal () using namespace std::placeholders; this ->timer_->cancel (); if (!this ->client_ptr_->wait_for_action_server (std::chrono::seconds (10 ))) { RCLCPP_ERROR (this ->get_logger (), "Action server not available after waiting" ); rclcpp::shutdown (); return ; } auto goal_msg = MoveRobot::Goal (); goal_msg.distance = 10 ; RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "Sending goal" ); auto send_goal_options = rclcpp_action::Client<MoveRobot>::SendGoalOptions (); send_goal_options.goal_response_callback = std::bind (&ActionControl01::goal_response_callback, this , _1); send_goal_options.feedback_callback = std::bind (&ActionControl01::feedback_callback, this , _1, _2); send_goal_options.result_callback = std::bind (&ActionControl01::result_callback, this , _1); this ->client_ptr_->async_send_goal (goal_msg, send_goal_options); } private : rclcpp_action::Client<MoveRobot>::SharedPtr client_ptr_; rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_; void goal_response_callback (GoalHandleMoveRobot::SharedPtr goal_handle) if (!goal_handle) { RCLCPP_ERROR (this ->get_logger (), "Goal was rejected by server" ); } else { RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "Goal accepted by server, waiting for result" ); } } void feedback_callback ( GoalHandleMoveRobot::SharedPtr, const std::shared_ptr<const MoveRobot::Feedback> feedback) RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "Feedback current pose:%f" , feedback->pose); } void result_callback (const GoalHandleMoveRobot::WrappedResult& result) switch (result.code) { case rclcpp_action::ResultCode::SUCCEEDED: break ; case rclcpp_action::ResultCode::ABORTED: RCLCPP_ERROR (this ->get_logger (), "Goal was aborted" ); return ; case rclcpp_action::ResultCode::CANCELED: RCLCPP_ERROR (this ->get_logger (), "Goal was canceled" ); return ; default : RCLCPP_ERROR (this ->get_logger (), "Unknown result code" ); return ; } RCLCPP_INFO (this ->get_logger (), "Result received: %f" , result.result->pose); } }; }; int main (int argc, char ** argv) rclcpp::init (argc, argv); auto action_client = std::make_shared <ActionControl01>("action_robot_cpp" ); rclcpp::spin (action_client); rclcpp::shutdown (); return 0 ; }
改写软件包的CMakeLists.txt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 find_package (ament_cmake REQUIRED)find_package (rclcpp REQUIRED)find_package (robot_control_interfaces REQUIRED)find_package (example_interfaces REQUIRED)find_package (rclcpp_action REQUIRED)add_executable (action_robot_01 src/robot.cpp src/action_robot_01.cpp ) target_include_directories (action_robot_01 PUBLIC $<BUILD_INTERFACE:${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR} /include > $<INSTALL_INTERFACE:include >) target_compile_features (action_robot_01 PUBLIC c_std_99 cxx_std_17) ament_target_dependencies( action_robot_01 "rclcpp" "rclcpp_action" "robot_control_interfaces" "example_interfaces" ) install (TARGETS action_robot_01 DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME} ) add_executable (action_control_01 src/action_control_01.cpp ) target_include_directories (action_control_01 PUBLIC$<BUILD_INTERFACE:${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR} /include > $<INSTALL_INTERFACE:include >) target_compile_features (action_control_01 PUBLIC c_std_99 cxx_std_17) ament_target_dependencies( action_control_01 "rclcpp" "rclcpp_action" "robot_control_interfaces" "example_interfaces" ) install (TARGETS action_control_01DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME} )